Urticaria
Introduction:
Urticaria, also known as hives, is a common skin condition that affects people of all ages in India. It is characterized by itchy, red, and swollen welts on the skin, resembling mosquito bites. Urticaria can be bothersome and may appear suddenly due to various triggers. In this article, we will explore what Urticaria is, its classification, signs, and symptoms, causes, risk factors, types, diagnostic tests, treatments, and complications, all explained in simple language for 10-year-old children to easily understand.
What Is Urticaria? :
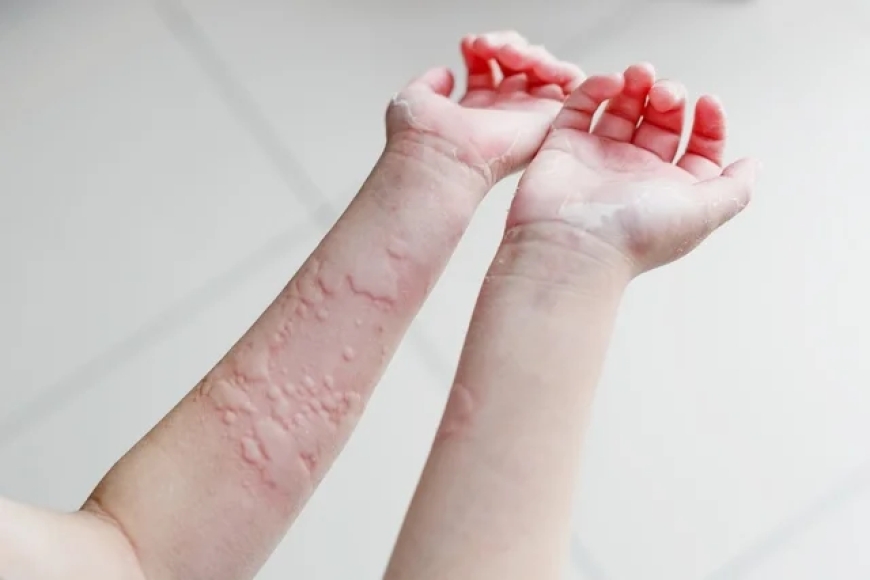
Urticaria is a skin rash characterized by raised, red, and itchy welts on the skin. These welts, also known as hives, can vary in size and shape and may appear on any part of the body. They are caused by the release of histamines, chemicals that cause the skin to swell and become irritated.
Signs and Symptoms:
- Red, Itchy Welts: The primary symptom of Urticaria is the appearance of red, itchy welts on the skin.
- Swelling: The welts may be swollen and may change in size and shape over time.
- Burning Sensation: Some individuals may experience a burning or stinging sensation in the affected areas.
How Is Urticaria Classified? :
Urticaria can be classified based on its duration:
- Acute Urticaria: Lasts for less than six weeks and is often caused by allergies or infections.
- Chronic Urticaria: Persists for more than six weeks and may have an underlying autoimmune cause.
Causes and Triggers:
Urticaria can be caused by various factors, including:
- Allergies: Allergens like certain foods, medications, pollen, or insect stings can trigger Urticaria.
- Infections: Viral or bacterial infections can also lead to the development of hives.
- Stress: Emotional stress or anxiety may worsen existing Urticaria or trigger new flare-ups.
Risk Factors with Examples:
Anyone can develop Urticaria, but certain risk factors may increase the likelihood:
- Food Allergies: Allergies to foods like nuts, shellfish, or eggs can trigger Urticaria.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as antibiotics or pain relievers, may cause hives in some individuals.
- Family History: A family history of Urticaria or other allergic conditions can increase the risk.
Types of Urticaria:
- Acute Urticaria: Lasts for a short duration, usually caused by allergies or infections.
- Chronic Urticaria: Persists for more than six weeks and may have no obvious trigger.
Diagnostic Tests and Treatments:
- Physical Examination: Doctors diagnose Urticaria by examining the skin and assessing the rash's appearance.
- Allergy Tests: If an allergy is suspected, skin or blood tests may be conducted to identify the allergen.
- Antihistamines: Medications like antihistamines are commonly prescribed to relieve itching and reduce swelling.
- Avoiding Triggers: Identifying and avoiding triggers can help prevent future flare-ups of Urticaria.
Complications of Urticaria:
While Urticaria is generally not life-threatening, it can be uncomfortable and may interfere with daily activities if left untreated. Severe cases may require medical attention to prevent complications.
Urticaria, or hives, is a common skin condition in India that causes itchy, red welts on the skin. By identifying triggers and seeking appropriate treatments, individuals with Urticaria can manage their condition effectively and lead a comfortable life. If you or your child experience symptoms of Urticaria, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and guidance.
What's Your Reaction?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0